概述
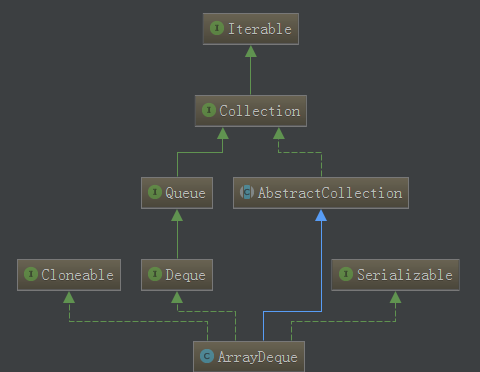
Deque是Queue的子接口,我们知道Queue是一种队列形式,而Deque则是双向队列,它支持从两个端点方向检索和插入元素,因此Deque既可以支持LIFO形式也可以支持LIFO形式.Deque接口是一种比Stack和Vector更为丰富的抽象数据形式,因为它同时实现了以上两者 ArrayDeque实现了Deque的接口以及上图其他的接口,因此ArrayDeque支持序列化、克隆、迭代器操作、队列特性并且扩展了AbstractCollection抽象类
应用场景
- linkedList内部实现用node节点链接前后元素。模拟c/c++的链表(长处在于中间节点的增删操作为o(1))。
- vector方法加着synchronized修饰(同步将带来性能的损耗)。Stack的实现又继承自vector,问题同上。
- ArrayDeque的底层实现为单纯的数组操作。所以单从性能上看。ArrayDeque在优于他们。当然因为
没有做同步处理,所以存在并发问题。须要调用方自己保障。
数组非循环队列到循环的理论
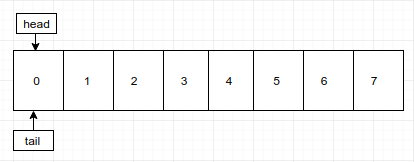
队列的数据结构,可以采用链表或者数组实现,但都需要2个指针分别代表队头(head)和队尾(tail)。目前采用数组实现,即用数组的下标分别代表。
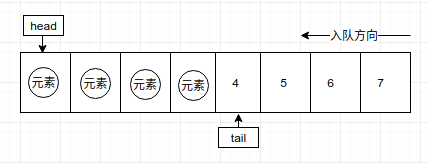
1. 默认都是head和tail都是索引为0的位置。如下图
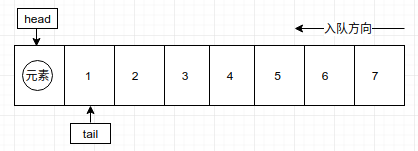
2. 当有新的元素入队时,head始终指向初始位置(即数组索引为0的位置),tail指向队列最后一个元素的下一个位置如图:
第一个元素入队
第二个元素入队
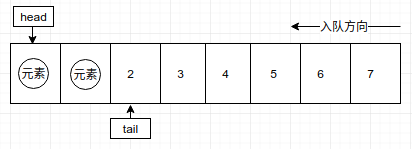
第n个元素入队
3. 当元素需要出队时,head需要指向下一个元素的索引位置,如图:
元素出队
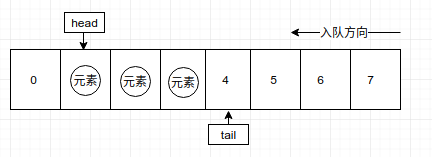
对于这种方式入队和出队,队空的判断条件显然是head=tail,队满的判断条件是tail=array.length(数组最后一个位置的下一位置)。显然,这种结构最致命的缺陷就是,tail只知道向后移动,一旦到达数组边界就认为队满,但是队列可能时刻在出队,也就是前面元素都出队了,tail也不知道
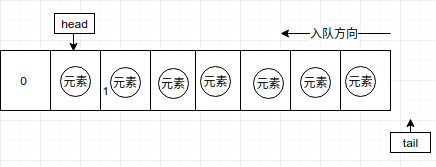
4. 当元素全部填充满时,暂不考虑自动扩容:如下图,
5. 当不在有入队,不断的出队,只剩最后一个元素时,此时如下图:
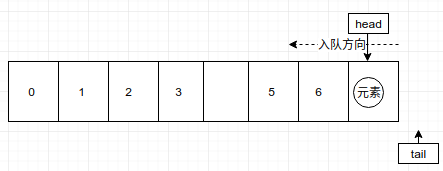
此时tail依然通过判断,认为队满,不能入队,这时数组的利用率我们是不能接受的,这样浪费很大。所以,我们引入循环队列,
6. tail可以通过mode数组的长度实现回归初始位置。 按照我们的想法,一旦tail到达数组边界,那么可以通过与数组长度取模返回初始位置,这种情况下判断队满的条件为tail=head
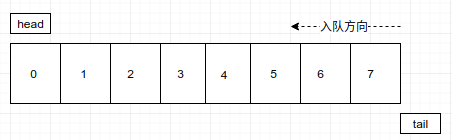
此时tail的值为8,取模数组长度8得到0,发现head=tail,此时认为队列满员。这是合理的,但是我们忽略了一个重要的点,判断队空的条件也是head=tail,那么该怎么区分是队空还是队满呢?解决办法是,空出队列中一个位置,如果(tail+1)%array.length=head,我们就认为队满,下面说明其合理性。
上面遇到的问题是,tail指向了队尾的后一个位置,也就是新元素将要被插入的位置,如果该位置和head相等了,那么必然说明当前状态已经不能容纳一个元素入队(间接的说明队满)。因为这种情况是和队空的判断条件是一样的,所以我们选择舍弃一个节点位置,tail指向下一个元素的位置,我们使用tail+1判断下一个元素插入之后,是否还能再加入一个元素,如果不能了说明队列满,不能容纳当前元素入队(其实还剩下一个空位置),看图:
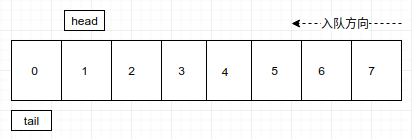
tail通过取模,回归到初始位置,我们判断tail+1是否等于head,如果等于说明队满,不允许入队操作,当然这是牺牲了一个节点位置来实现和判断队空的条件进行区分。
JDK中的ArrayDeque
ArrayDeque中几个重要的属性
1 /**
2 * The array in which the elements of the deque are stored.
3 * The capacity of the deque is the length of this array, which is
4 * always a power of two. The array is never allowed to become
5 * full, except transiently within an addX method where it is
6 * resized (see doubleCapacity) immediately upon becoming full,
7 * thus avoiding head and tail wrapping around to equal each
8 * other. We also guarantee that all array cells not holding
9 * deque elements are always null.
10 */
11 transient Object[] elements; // non-private to simplify nested class access
12
13 /**
14 * The index of the element at the head of the deque (which is the
15 * element that would be removed by remove() or pop()); or an
16 * arbitrary number equal to tail if the deque is empty.
17 */
18 transient int head;
19
20 /**
21 * The index at which the next element would be added to the tail
22 * of the deque (via addLast(E), add(E), or push(E)).
23 */
24 transient int tail;
25
26 /**
27 * The minimum capacity that we'll use for a newly created deque.
28 * Must be a power of 2.
29 */
30 private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;
摘自jdk1.8
- elements: 绍用于存储队列中每个节点,不过在ArrayDeque中该数组长度是没有限制的,采用一种动态扩容机制实现动态扩充数组容量
- head和tail分别代表着头指针和尾指针
- MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY代表着创建一个队列的最小容量
ArrayDeque的构造器
1 /**
2 * Constructs an empty array deque with an initial capacity
3 * sufficient to hold 16 elements.
4 */
5 public ArrayDeque() {
6 elements = new Object[16];
7 }
8
9 /**
10 * Constructs an empty array deque with an initial capacity
11 * sufficient to hold the specified number of elements.
12 *
13 * @param numElements lower bound on initial capacity of the deque
14 */
15 public ArrayDeque(int numElements) {
16 allocateElements(numElements);
17 }
18 /**
19 * Constructs a deque containing the elements of the specified
20 * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
21 * iterator. (The first element returned by the collection's
22 * iterator becomes the first element, or <i>front</i> of the
23 * deque.)
24 *
25 * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into the deque
26 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
27 */
28 public ArrayDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
29 allocateElements(c.size());
30 addAll(c);
31 }
摘自jdk1.8
如果没有指定显式传入elements的长度,则默认16。如果显式传入一个代表elements的长度的变量,那么会调用allocateElements做一些简单的处理,并不会简单的将你传入的参数用来构建elements,它会获取最接近numElements的2的指数值,比如:numElements等于20,那么elements的长度会为32,numElements为11,那么对应elements的长度为16。但是如果你传入一个小于8的参数,那么会默认使用我们上述介绍的静态属性值作为elements的长度。至于为什么这么做,因为这么做会大大提高我们在入队时候的效率(此处是重点,在判断是否扩容提升判断的性能),还支持将元素集批量入队。
入队操作
由于ArrayDeque实现了Deque,所以它是一个双向队列,支持从头部或者尾部添加节点,由于内部操作类似,我们只简单介绍从尾部添加入队操作。涉及以下一些函数:
1 /**
2 * Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
3 *
4 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
5 *
6 * @param e the element to add
7 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
8 */
9 public void addLast(E e) {
10 if (e == null)
11 throw new NullPointerException();
12 elements[tail] = e;
13 if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
14 doubleCapacity();
15 }
16 /**
17 * Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
18 *
19 * @param e the element to add
20 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast})
21 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
22 */
23 public boolean offerLast(E e) {
24 addLast(e);
25 return true;
26 }
27 /**
28 * Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
29 *
30 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
31 *
32 * @param e the element to add
33 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
34 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
35 */
36 public boolean add(E e) {
37 addLast(e);
38 return true;
39 }
主要的方法还是addLast,该方法首先将你要添加的元素入队,然后通过这条语句判断队是否已满:
1 if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
这条语句的判断条件还是比较难理解的,我们之前在构造elements元素的时候,说过它的长度一定是2的指数级,所以对于任意一个2的指数级的值减去1之后必然所有位全为1,例如:8-1之后为111,16-1之后1111。
而对于tail来说,当tail+1小于等于elements.length -1,两者与完之后的结果还是tail+1,但是如果tail+1大于elements.length-1,两者与完之后就为0,回到初始位置。
这种判断队列是否满的方式要远远比我们使用符号%直接取模高效,jdk优雅的设计从此可见一瞥。接着,如果队列满,那么会调用方法doubleCapacity扩充容量,
1 /**
2 * Doubles the capacity of this deque. Call only when full, i.e.,
3 * when head and tail have wrapped around to become equal.
4 */
5 private void doubleCapacity() {
6 assert head == tail;
7 int p = head;
8 int n = elements.length;
9 int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
10 int newCapacity = n << 1;
11 if (newCapacity < 0)
12 throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
13 Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
14 System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
15 System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
16 elements = a;
17 head = 0;
18 tail = n;
19 }
首先会获取到原数组长度,扩大两倍构建一个空数组,接下来就是将原数组中的内容移动到新数组中
出队操作
出队操作和入队一样,具有着多个不同的方法,但是内部调用的还是一个pollFirst方法,我们主要看下该方法的具体实现即可:
1 public E pollFirst() {
2 int h = head;
3 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
4 E result = (E) elements[h];
5 // Element is null if deque empty
6 if (result == null)
7 return null;
8 elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
9 head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
10 return result;
11 }
该方法很简单,直接获取数组头部元素即可,然后head往后移动一个位置。这是出队操作,其实删除操作也是一种出队,内部还是调用了pollFirst方法:
1 /**
2 * @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
3 */
4 public E removeFirst() {
5 E x = pollFirst();
6 if (x == null)
7 throw new NoSuchElementException();
8 return x;
9 }
其他的一些操作 我们可以通过getFirst()或者peekFirst()获取队头元素(不删除该元素,只是查看)。toArray方法返回内部元素的数组形式。
1 /**
2 * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this deque
3 * in proper sequence (from first to last element).
4 *
5 * <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
6 * maintained by this deque. (In other words, this method must allocate
7 * a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
8 *
9 * <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
10 * APIs.
11 *
12 * @return an array containing all of the elements in this deque
13 */
14 public Object[] toArray() {
15 return copyElements(new Object[size()]);
16 }
还有一些利用索引或者值来检索具体节点的方法,由于这些操作并不是ArrayDeque的优势,
总结
ArrayDeque的主要优势在于尾部添加元素,头部出队元素的效率是比较高的,内部使用位操作来判断队满条件,效率相对有所提高,并且该结构使用动态扩容,所以对队列长度也是没有限制的。在具体情况下,适时选择。


评论